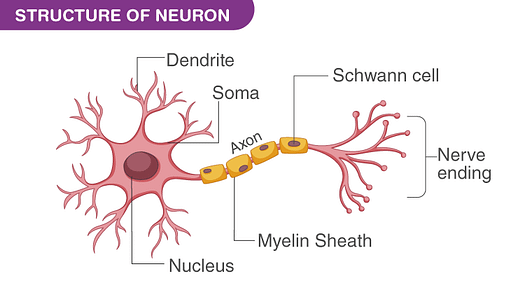
Neurons are specialized cells that can transmit electrical and chemical impulses. If you think of the brain as a circuit, then dendrites and axons can be thought of as wires and the cell body as a component.
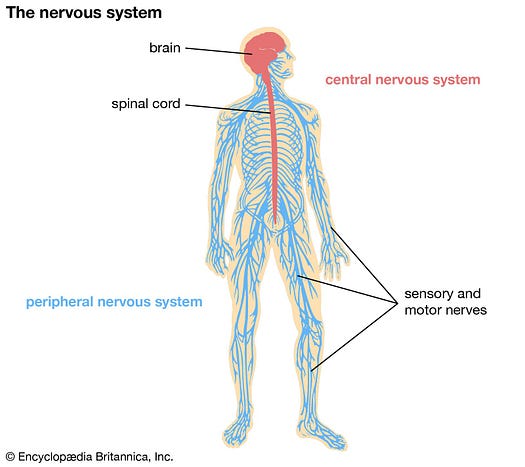
It is a cell found in the central and peripheral nervous system. Central nervous system (CNS) is made up of the brain and spinal cord while peripheral nervous system (PNS) consists of the nerves coming to and from the CNS.
If a neuron receives a large number of inputs from other neurons, these signals add up until they exceed a specific threshold. Once the threshold is exceeded, the neuron is triggered to send an impulse along its axon. This impulse is called action potential.
What is an action potential?
It is created by the movement of electrically charged atoms (or ions) across the axon’s membrane. It is also called a spike which means rapid rise and fall of the membrane potential. This is what the ele
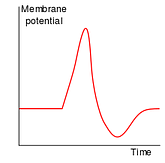
When the cell body of a nerve cell receives enough signals to trigger it to fire, a portion of the axon depolarizes.
Wait, wait….
What is depolarization?
Well, polarization means separation of charges (poles). So depolarization means unification of charges.
Concentration gradients is the difference in ion concentrations between the inside and outside of a neuron. Neurons have a negative potential gradient most of the time, meaning there are more positively charged ions outside than inside the cell. This regular state is called resting membrane potential.
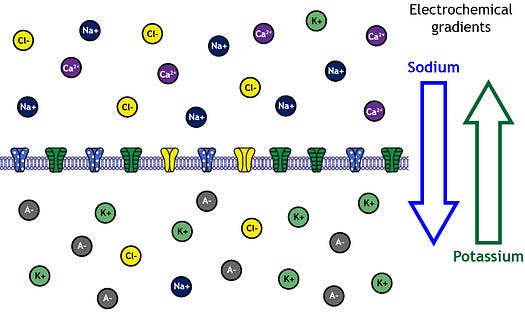
During the resting membrane potential:
- More Sodium ions (Na+) outside than inside the neuron.
- More Potassium ions (K+) inside than outside the neuron.
When an action potential is triggered, the gated ion channels open, allowing Na+ ions to flow into the cell body. These ions pass through channels that open when neurotransmitters bind to the channel and tells it to open. Once one channel opens, it’s like tipping over a trail of dominoes as it sets the stage for other channels to do the same.
As the initial potential was negative, the unification of charges causes the potential to be zero. This is the rise in the spike.
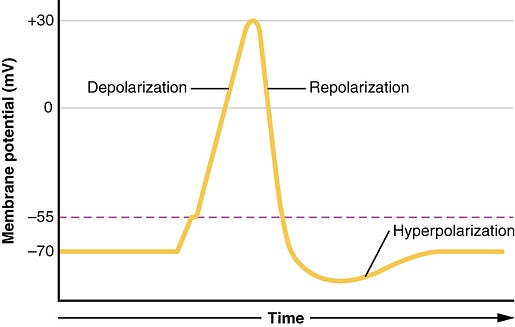
Repolarization brings the cell back to its resting potential. The gated sodium channels close. At the same time, the potassium channels open. There are more Potassium ions inside than out, so more Potassium exits than comes in. As positive ions exit the cell, the cell returns to its resting state.
Hyperpolarization: As potassium channels open longer than they should, the cell becomes more negative than its resting state (due to excess separation of charges). The sodium-potassium pump works to push sodium out and take potassium in.
What is a Synapse?
Neurons communicate with each other using synapses. They are messages sent between neurons.

They may be chemical: release of a neurotransmitter, or electrical: ions directly flow between cells.
During a chemical synapse, when the impulse reaches the end of neurons, neurotransmitters are secreted by the pre-synaptic neuron into the synaptic cleft. The neurotransmitters bind on the post-synaptic neurons to trigger an action potential in the next cell!
That’s it for today! Keep reading, keep learning!





